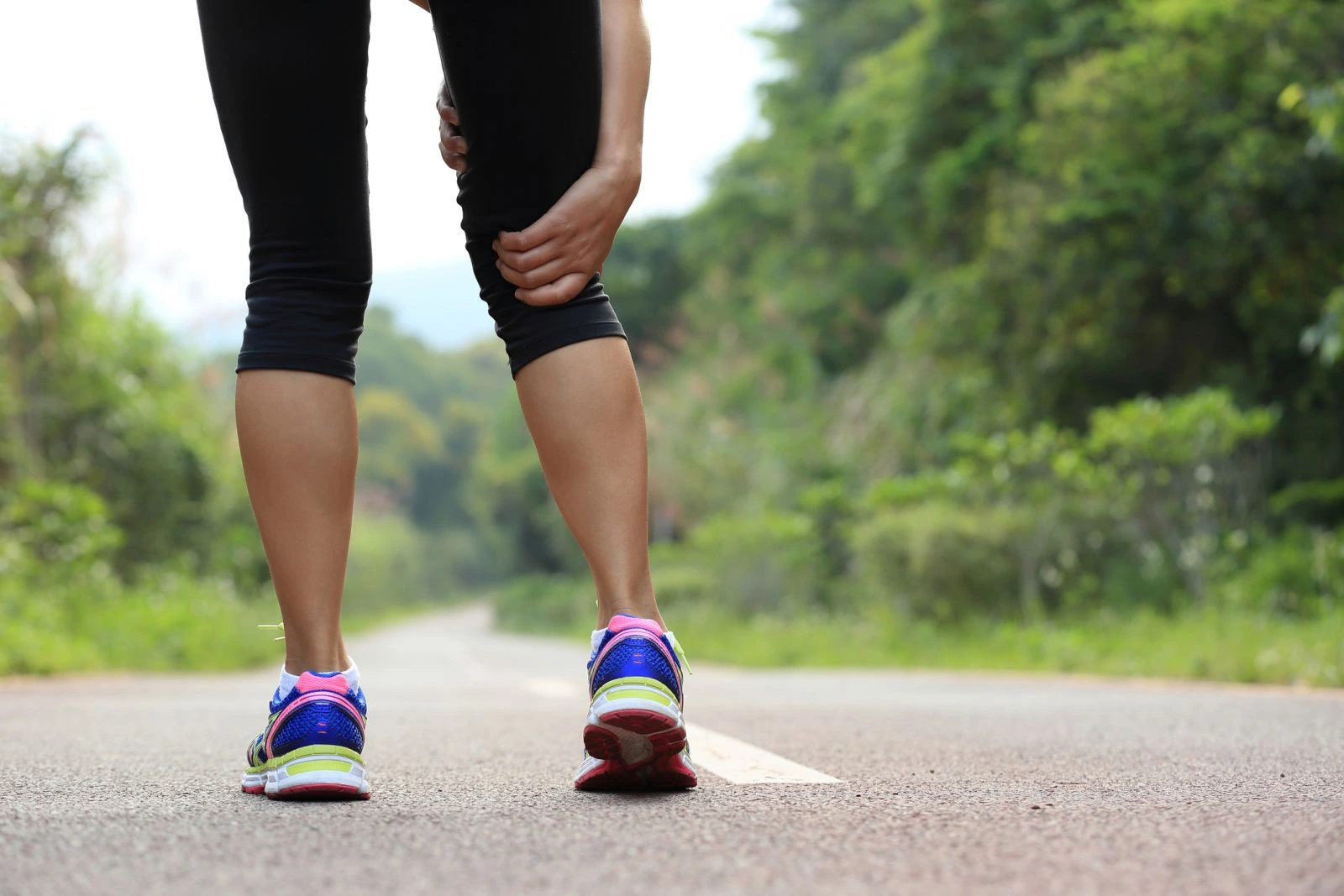
Understanding PAD: Recognizing the hidden obstacles in your Arteries
Learn about Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), a serious yet often overlooked condition affecting millions worldwide. Discover its causes, symptoms, treatments, and why early diagnosis is key to prevention—especially during PAD Awareness Month.
- Concept Editor

You’re all set with heart health and stroke, but what about Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)? September marks as Peripheral Artery Disease Awareness (PAD) month, highlighting the need for better recognise of this serious condition. Peripheral Artery Disease cause around 200 million people globally particularly those over 50. Despite its treatability, many cases go undiagnosed as symptoms are often mistaken for other issues. Awareness and early diagnosis are crucial to prevent severe complications, such as limb amputations. This month, we focus on understanding Peripheral Artery Disease causes, symptoms, and treatment options to promote better management and prevention strategies.
What is Peripheral Artery Disease?
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a vascular condition where arteries outside the heart and brain narrow, commonly affecting the legs.
- This narrowing restricts blood flow, causing symptoms like leg pain (claudication), numbness, and non-healing sores. Peripheral Artery Disease often results from atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits build up in the arteries. If untreated, it can lead to severe complications, including limb amputation.
How is Peripheral Artery Disease Caused?
- Peripheral Artery Disease is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits, cholesterol and other substances builds in and on the artery walls, this buildup is called Plaque. These Plaque can harden and narrows the arteries, reducing or completely blocking the flow of oxygen-rich blood to vital organs and limbs. Several factors contribute to development of atherosclerosis and, consequently, PAD:
- Smoking: Tobacco use generally speeds up the process of artery damage and plaque buildup.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar level can damage the blood vessel and can increase the formation of Plaque.
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can damage arterial wall increase the risk of plaque formation.
- High Cholesterol: High levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) can lead to plaque formation in the arteries.
- Inactive lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to poor cardiovascular health and increased risk of Peripheral Artery Disease.
- Obesity: Excess weight can lead to a range of health problems, including high blood pressure and diabetes, which are risk factors for Peripheral Artery Disease.
What are the Symptoms of Peripheral Artery Disease?
About 1 in 4 people with Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) experience common factors. Regardless of symptoms everyone with PAD is at risk for cardiovascular disease.
- Leg Pain: Pain or cramping in legs or buttocks while walking or climbing stairs known as claudication, which typically improves with rest.
- Numbness or Weakness: Sensation of numbness or weakness in legs or feet.
- Coldness: Coldness in lower feet, than rest of the body.
- Sores or wounds: Slow healing sores or wounds on toes, feet, or legs.
- Change of colour: Change in skin colour such as a bluish or pale appearance of the legs or feet.
- Reduced Pulse: Weak or absent pulse in the legs or feet, which can be detected by a healthcare provider.
How is Peripheral Artery Disease Treated?
Preventing Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) address risk factors. And adopting Healthy lifestyle. Here are some key strategies to prevent from:
- Quite Smoking: Smoking is a major factor for Peripheral Artery Disease stopping smoking improves overall vascular health and reduce the risk of PAD.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet reach in Fruits, vegetables, Whole grains and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. This helps in maintain blood cholesterol level reduces plaque buildup in arteries.
- Exercise Regular: Engage in regular activities, such as cycling or walking to improve circulation and strengthen in cardiovascular system.
- Manage Blood pressure: Keep your blood pressure within a healthy range.
- Manage Blood Sugar level: If you have diabetes or prediabetes, managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication is crucial to reduce the risk of Peripheral Artery Disease.
What is the Surgical Solution?
In severe cases of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), revascularization procedures may be recommended to restore blood flow. This is considered when leg pain hinders daily activities or other treatments have failed. There are two main types:
- Angioplasty – A balloon is inflated inside a narrowed artery to widen it. Concept Medical is a leader in this field, offering advanced SCB (Sirolimus Coated Balloon) technology our innovative products:
- MagicTouch PTA: (Sirolimus Coated PTA Balloon Catheter) for peripheral arterial disease
- Artery Bypass Graft – Blood vessels from another part of the body are used to bypass the blockage in the artery.
Conclusion
September’s PAD Awareness Month highlights the importance of early detection and management. Addressing risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. Effective management is essential for improving outcomes and quality of life.
References
- Foundation to Advance Vascular Cures: – Peripheral Artery Disease | The Foundation to Advance Vascular Cures
- Mayo Clinic:- Peripheral artery disease (PAD) – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
- Healthline:- Peripheral Vascular Disease: Types, Causes, and Risk Factors (healthline.com)
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute: – Peripheral Artery Disease – Symptoms | NHLBI, NIH
- Azuravascularcare:- Peripheral Artery Disease, (PAD) | Are you at Risk? (azuravascularcare.com)
- Wikipedia: – Peripheral artery disease – Wikipedia
You may also like

5 min